Managing Food Allergies or Intolerances
Effective Strategies and Tips
Discover > Healthy Living Through Food > Managing Food Allergies or Intolerances
In today's diverse world, more people than ever are affected by food allergies or intolerances. These conditions can range from mild to severe and can greatly impact the quality of life for those who experience them. However, with proper understanding and management strategies, it is possible to live a healthy and fulfilling life while still navigating the challenges of food allergies and intolerances.
To successfully manage food allergies or intolerances, individuals must first identify the specific triggers that cause their adverse reactions. This usually requires the assistance of healthcare professionals and may involve allergy testing or food elimination diets. Once the problematic foods have been recognized, the next step involves learning how to avoid these dietary triggers while still maintaining balanced and nutritious meals.
Managing food allergies or intolerances is essential for a child's well-being. Recognizing food allergy symptoms and identifying the specific food allergen causing them is crucial in preventing a severe allergic reaction. Understanding and carefully monitoring a child's food allergy can help ensure their safety and enable informed choices about what they eat, creating a safer and healthier environment for them.
Education and awareness play a crucial role in managing food allergies or intolerances. Individuals must become informed about label reading, cross-contamination risks, and dietary alternatives to ensure they can safely consume meals without compromising their health. By combining knowledge and vigilance, those with food allergies or intolerances can confidently tackle this challenge and lead fulfilling lives.
Understanding Food Allergies
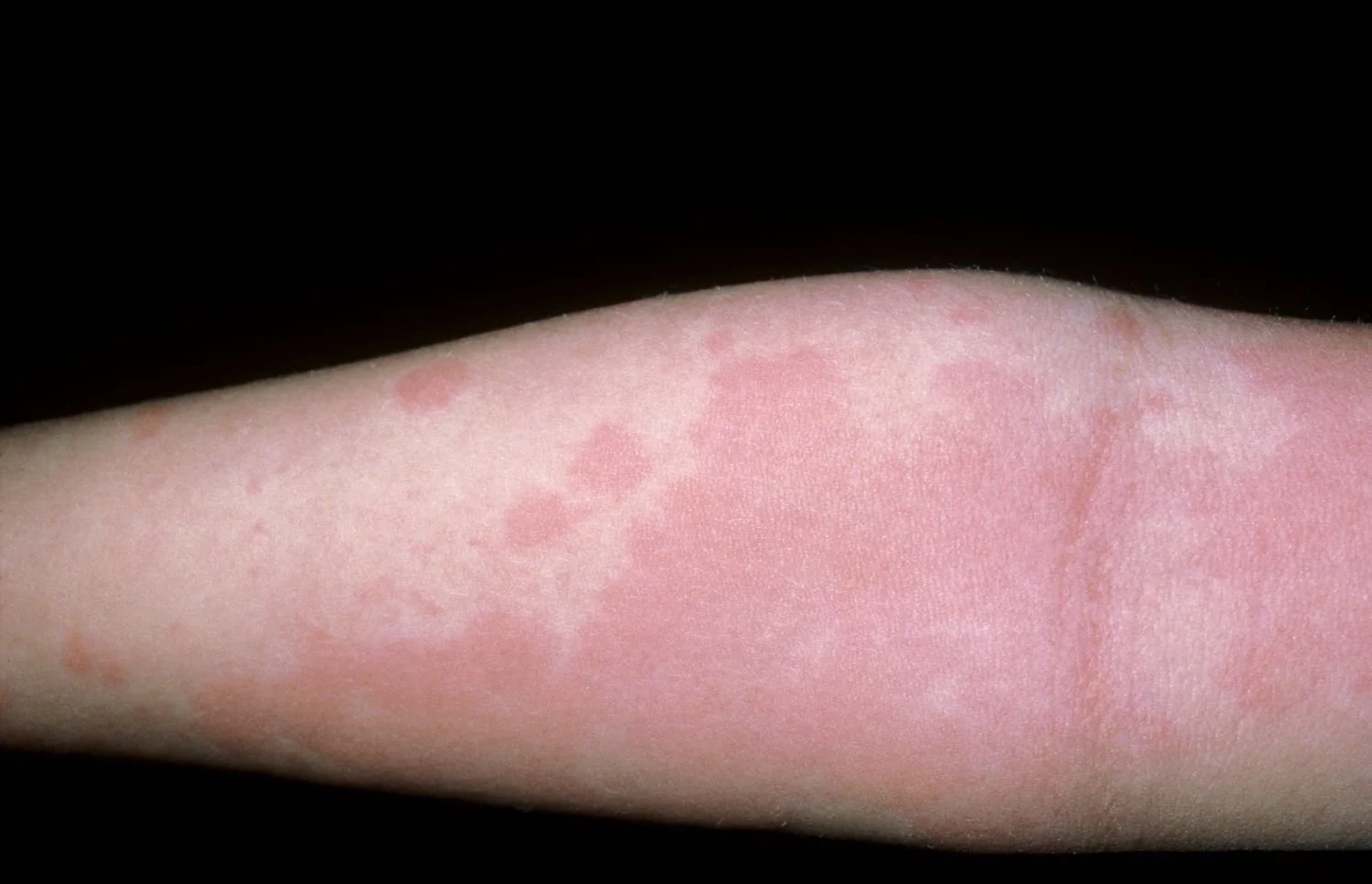
Food allergies occur when the immune system misidentifies a harmless food protein as a threat and reacts accordingly. These reactions can range from mild to severe, with symptoms such as skin rashes, gastrointestinal issues, and even life-threatening anaphylaxis.
There are several common food allergens, including:
Milk
Eggs
Tree nuts (e.g., almonds (how long do almonds last?), walnuts (how long do walnuts last?), cashews)
Fish
Shellfish (What wine goes well with shellfish?)
Soy
Wheat
However, it is essential to note that individuals can develop allergies to any food. Allergic reactions typically occur within minutes to hours after ingesting the allergen, and the severity of symptoms can vary based on individual sensitivities and the amount of allergen consumed.
In addition to allergies, some people may also experience food intolerances, which involve a different type of immune system response. Unlike allergies, intolerances do not involve a life-threatening reaction or anaphylaxis. Instead, they often result in digestive symptoms, such as bloating, gas, or diarrhea. Examples of common food intolerances include lactose intolerance and gluten sensitivity.
Managing food allergies and intolerances requires vigilance and proactive measures. This includes reading food labels carefully, communicating with food servers and chefs at restaurants, and carrying appropriate medications such as antihistamines or epinephrine injectors for those with severe allergies.
Furthermore, working with a healthcare professional or allergist can help individuals develop a personalized plan to avoid allergens, minimize symptoms, and ensure a balanced diet.
Differentiating Between Allergy and Intolerance
Food allergies and intolerances may share similar symptoms, but they are distinct conditions. Understanding their differences is crucial for proper management and treatment.
Food allergies
Food allergies are an immune system reaction to certain food proteins. They occur when the immune system mistakenly identifies these proteins as harmful. In response, the body produces antibodies called Immunoglobulin E (IgE), which trigger a release of histamine and other chemicals. This release causes allergic symptoms that can range from mild to life-threatening. Common food allergens include milk, eggs, peanuts, tree nuts, soy, wheat, fish, and shellfish.
Food intolerances
Food intolerances, on the other hand, do not involve the immune system. They are an inability to properly digest or metabolize specific foods or components. This may happen due to enzyme deficiencies, sensitivity to certain chemicals, or other factors that alter the gut's processing of the food. The symptoms of food intolerances are usually less severe than allergies and are predominantly gastrointestinal. Lactose intolerance, where individuals cannot break down the sugar found in milk products, is a common example.
While both conditions may cause abdominal pain, diarrhea, and nausea, there are differences in the presentation of symptoms. Allergic reactions often have a rapid onset and may also include swelling, hives, and breathing difficulties. Intolerances manifest more slowly, typically taking hours to appear and primarily affecting the digestive system.
Diagnosis and management also vary between these conditions. For food allergies, skin prick tests, blood tests for IgE antibodies, and oral food challenges conducted by healthcare professionals help determine the specific allergens.
Strict avoidance of allergenic food and awareness of potential cross-contamination is essential. Patients are advised to carry an epinephrine auto-injector to counter severe allergic reactions (anaphylaxis).
On the other hand, food intolerances are commonly diagnosed through elimination diets and reintroduction tests, where the suspected food is removed and gradually added back to assess the presence of symptoms. In some cases, enzyme replacements or other supplements can help manage the intolerance; however, it may still be necessary to limit or avoid trigger foods.
Identifying Food Allergies and Intolerances
Symptoms of Food Allergies
Food allergies can manifest in various ways, and the severity of reactions can vary from person to person. Common symptoms include:
Swelling: Facial swelling, including the eyes and lips, is a common reaction to allergenic foods.
Skin reactions: These may include hives, itching, and redness.
Breathing difficulties: Asthma-like symptoms, such as shortness of breath, wheezing, and coughing, may occur.
Gastrointestinal symptoms: Stomach pain, vomiting, diarrhea, and nausea are typical reactions to food allergens.
Anaphylaxis: A severe and potentially life-threatening reaction that can cause sudden blood pressure drops, rapid pulse, and constriction of the airways.
It is important to note that reaction times can vary; some people may experience symptoms within minutes of consumption, while others may take several hours.
Symptoms of Food Intolerances
While food intolerances are not life-threatening like food allergies, they can cause uncomfortable symptoms. These may include:
Bloating: Excess gas production due to the body's inability to digest certain components of the food.
Diarrhea: Often caused by malabsorption of specific food components, such as lactose or fructose.
Constipation: Certain intolerances can cause the slowing down of the digestive process, leading to constipation.
Gastrointestinal pain: Cramps and stomach pain are typical symptoms of food intolerances.
Headaches and migraines: Intolerances of substances like tyramine in aged cheese or sulfites in wine can cause these symptoms.
To identify food allergies and intolerances, individuals should consult a healthcare professional or allergist, who will be able to conduct tests and provide guidance on managing symptoms effectively.
Testing for Food Allergy and Intolerance
Skin Prick Test
The Skin Prick Test is a common method for identifying food allergies. During this test, a small amount of the suspected allergen is placed on the patient's skin, which is then pricked with a needle. If the patient experiences a reaction, such as redness or swelling, it indicates that the person may have an allergy to the specific substance.
Blood Test
Blood tests can also be used to check for food allergies and intolerances. In this case, a sample of the patient's blood is taken and tested for the presence of specific antibodies that are associated with a reaction to certain foods. A positive result suggests that the individual might have an allergy or intolerance to the specific food.
Elimination Diet
An Elimination Diet can be an effective way to identify food allergies and intolerances. This involves the patient gradually removing certain foods from their daily meal plan for a period and then reintroducing them one by one. If a reaction occurs after reintroducing a specific food, it could indicate a possible intolerance or allergy. This process should be done under the guidance of a healthcare professional to ensure proper execution and safety.
Managing and Living with Food Allergies and Intolerances
Diet Adjustments
One essential aspect of managing food allergies and intolerances is adjusting the diet. This typically involves eliminating the allergen or problematic food from consumption. It is crucial to read food labels carefully and understand their ingredients. Individuals should also be aware of cross-contamination risks when preparing meals. For those with intolerances, consuming food substitutes or supplements might help to alleviate symptoms.
Epinephrine Autoinjectors
For individuals with severe food allergies, carrying an epinephrine autoinjector is vital. Epinephrine helps to counteract life-threatening allergic reactions known as anaphylaxis. Ensure that the autoinjector is easily accessible and that the expiry date is checked regularly. It is also crucial to educate family members, friends, and colleagues on how to administer epinephrine in case of emergencies.
Developing an Action Plan
Creating an action plan helps individuals identify triggers and manage their food allergies or intolerances effectively. This plan should include:
Identifying allergens and possible cross-reactants
Knowing the signs and symptoms of allergic reactions
Learning how to administer epinephrine in case of anaphylaxis
Informing and educating those in close contact about the allergy or intolerance
Carrying essential medication and medical information at all times
By following these guidelines, individuals with food allergies and intolerances can lead healthier and safer lives.
Prevention of Food Allergies and Intolerances
Preventing food allergies and intolerances is important for individuals who experience adverse reactions to certain foods. Several strategies can be used to minimize the risk of developing food allergies or intolerances.
The first approach is to maintain a healthy gut and immune system. This can be achieved through a balanced diet, regular exercise, and incorporating probiotics into one's daily routine. Probiotics can help support healthy gut bacteria, which can reduce the risk of allergies and intolerances.
Another strategy is to introduce new foods to children at an early age. By diversifying an infant's diet, there's a lower chance of developing allergies to certain foods. For example, giving peanut products to infants at an early age has been found to decrease the risk of developing a peanut allergy later in life.
In addition to early exposure to potential allergens, practicing good hygiene is crucial in preventing food allergies and intolerances. This includes washing hands and surfaces before preparing food, as well as storing food properly to avoid contamination.
Lastly, individuals can follow an elimination diet if they suspect they have a food allergy or intolerance. This involves removing suspected foods from the diet for some time, and then reintroducing them to monitor symptoms and identify the culprit. It's important to consult a healthcare professional before starting an elimination diet to ensure proper guidance and support.
By utilizing these strategies, individuals can proactively manage their risk of developing food allergies and intolerances, promoting healthier and more enjoyable eating experiences.
Conclusion
Managing food allergies and intolerances is a crucial aspect of ensuring the safety and well-being of those affected. By following proper guidelines and practices, individuals can effectively cope with these challenges.
Firstly, education and awareness play a significant role in handling food allergies and intolerances. This involves understanding the difference between the two, knowing the common allergens and food triggers, and learning how to read food labels accurately.
Additionally, open communication with friends, co-workers, and dining establishments can help prevent unpleasant situations and create a supportive environment.
Another critical factor is seeking professional help, such as consulting with a doctor, allergist, or dietician who specializes in managing food allergies and intolerances. They can provide personalized advice, recommend appropriate tests and treatments, and ensure a balanced diet.
Individuals with food allergies or intolerances can lead fulfilling, healthy lives by staying well-informed, proactive, and resourceful. By actively managing their conditions and making informed decisions, they can minimize the risk of adverse reactions and enjoy a diverse range of foods.
A combination of vigilance, knowledge, and support from healthcare professionals is essential for successfully navigating these dietary challenges.
Have you ever wondered Is Chocolate Safe for Kids? Check out this guide.
This are Healthy Living Tips for Kid’s Nutrition. Check this Guide.